Disaster Recovery Management Explained

Disaster Recovery Management: Secure Success 2025
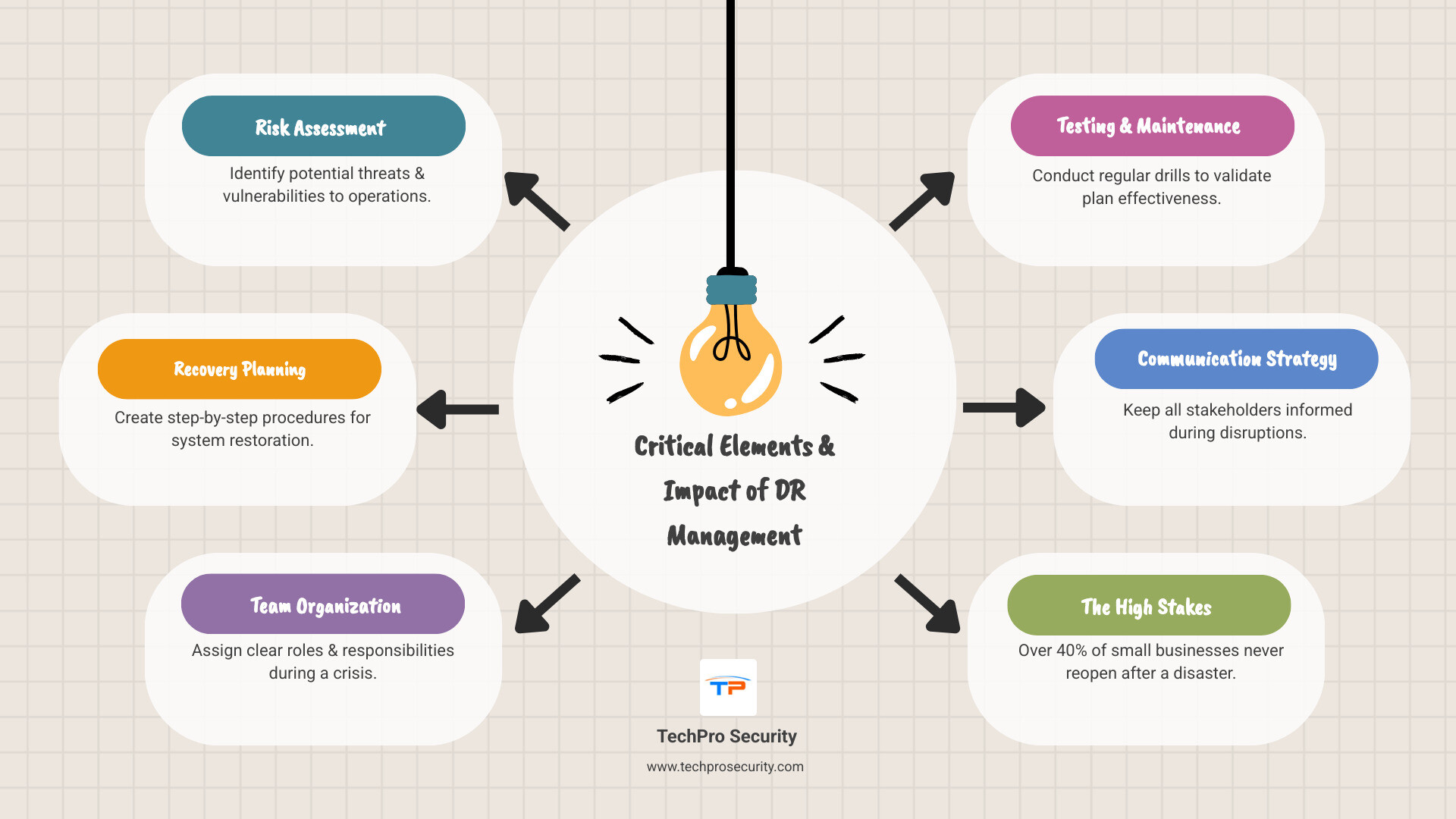
Disaster recovery management is the strategic process of ensuring your business can quickly recover from disruptive events. It involves several key elements:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential threats.
- Recovery Planning: Creating procedures for system restoration.
- Team Organization: Assigning roles for a crisis.
- Testing & Maintenance: Regular drills to ensure the plan works.
- Communication Strategy: Keeping stakeholders informed.
The stakes are incredibly high. Research shows infrastructure failure can cost $100,000 per hour, while critical application failures can cost $500,000 to $1 million per hour. Worse, more than 40% of small businesses never reopen after a disaster, and another 25% fail within a year.
Threats range from cyberattacks and natural disasters to hardware failures and human error. In today’s complex IT environments, a single point of failure can cause company-wide disruption. The good news is that a robust disaster recovery strategy minimizes downtime, protects your reputation, and ensures business continuity. The key is proactive planning.
I’m Brad Besner, and my experience founding security companies has shown me that proper disaster recovery management is the difference between survival and closure. At TechPro Security, we’ve learned that effective strategies combine thorough planning with modern technology.
Essential disaster recovery management terms:
Foundations of a Resilient DR Strategy
A resilient disaster recovery management strategy is built on a solid foundation. This means understanding your critical business functions, the risks you face, and your compliance requirements. Getting these fundamentals right is the first step to building a plan that works.
Understanding RTO, RPO, and Business Impact
Every effective disaster recovery management plan revolves around two crucial metrics: Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
To set these, you must first conduct a Business Impact Analysis (BIA). This involves identifying your most critical systems and understanding the consequences if they go down for an hour, a day, or a week.
- RTO answers: “How quickly do we need to be back up and running?” For a payment system, this might be minutes. For other systems, it could be hours.
- RPO answers: “How much data can we afford to lose?” This determines your backup frequency. If you can’t lose any transactions, you need constant data replication. If losing a day’s worth of data is acceptable, daily backups may suffice.
Objective Definition What it answers Impact on DR planning
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) Maximum acceptable downtime for systems/applications “How quickly must we be back online?” Determines recovery speed, technology choices (hot vs. cold sites), and failover mechanisms.
RPO (Recovery Point Objective) Maximum acceptable amount of data loss (age of data) “How much data can we afford to lose?” Influences backup frequency, replication methods, and data protection strategies.
This process forces you to prioritize. Not every system is mission-critical, allowing you to allocate resources more effectively. For a comprehensive look at this planning process, check out The Ultimate Guide to Disaster Recovery Planning | TechPro Security.
Identifying Potential Disasters and Risks
Being prepared means realistically assessing potential threats. The goal isn’t paranoia, but readiness.
- Natural Disasters: Here in South Florida, we know hurricanes well. Floods, earthquakes, and severe weather can halt operations anywhere.
- Cyberattacks: Ransomware and data breaches are increasingly common and target businesses of all sizes.
- Hardware Failures: Servers, hard drives, and networking equipment will eventually fail. It’s a matter of when, not if.
- Human Errors: Accidental deletions, misconfigurations, or falling for phishing scams can cause significant damage.
- Utility and Security Failures: Power outages can bring everything to a standstill, while physical security breaches (theft, sabotage) pose a direct threat to your infrastructure.
The smart approach is to focus on the consequences of these events (e.g., server is down) rather than every possible cause. This makes your recovery plan more versatile.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Disaster recovery management is often a legal requirement. Depending on your industry, a robust DR plan is mandatory for compliance.
- HIPAA: Healthcare organizations must ensure protected health information (PHI) is secure and accessible, even during a disaster.
- GDPR: Affects any business handling data from EU citizens, requiring strong data protection and recovery capabilities.
- PCI DSS: Businesses processing credit cards must maintain secure systems, including DR.
- Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX): Publicly traded companies must retain business records, necessitating reliable backup and recovery.
- SOC 2: Crucial for service organizations, this framework evaluates security, availability, and more. Physical security is a key component, which is where TechPro Security’s expertise in cameras and access control helps create robust physical barriers to protect data centers.
Your DR plan must include ways to maintain audit trails and generate compliance reports to prove you can recover securely. For more details, visit More on SOC 2 compliance and understand the different approaches at business continuity vs disaster recovery.
The Core Components of Disaster Recovery Management
Effective disaster recovery management requires the right people, processes, and communication channels working in harmony. A solid plan rests on three pillars: protecting your data, organizing your team, and keeping everyone informed. This coordination transforms a chaotic scramble into a measured recovery.

Critical Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Your data is the lifeblood of your business. A bulletproof backup strategy is central to disaster recovery management. We recommend the 3-2-1 backup strategy: keep 3 copies of your data on 2 different media types, with 1 copy offsite.
This strategy combines on-site backups for fast recovery from minor issues with off-site storage (often in the cloud) for protection against major disasters like fires or floods. Cloud solutions offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and geographic redundancy. Strong encryption is essential to protect data both in transit and at rest.
Your backup frequency should align with your Recovery Point Objective (RPO). Most importantly, regularly test your restoration process. A backup is useless if it can’t be restored. Too many businesses find their backups are corrupt only when it’s too late.
Our Cloud Backup and File Storage services help ensure your data is protected and recoverable.
Building Your Disaster Recovery Management Team
When a disaster occurs, clear roles prevent confusion and speed up recovery. A dedicated disaster recovery management team is essential.
- Crisis Management Leader: A senior executive who makes strategic decisions and handles external communications.
- IT Recovery Team: The technical experts (engineers, admins) who restore systems.
- Communications Coordinator: The single voice for managing updates to employees, customers, and the media.
- Department Liaisons: Bridges between the recovery team and business units to ensure all needs are met.
- Third-Party Contacts: An updated list of vendors, service providers, and emergency contacts.
Everyone must know their role before a crisis. Regular training and clear documentation are key. You’ll find more guidance on building effective teams through our IT Services.
The Importance of a Crisis Communication Plan
How you communicate during a crisis can be more important than the crisis itself. A solid communication plan is a non-negotiable part of disaster recovery management.
Your plan should define how you will notify all stakeholders:
- Employees: Need safety updates and work instructions through multiple channels (email, text, social media) in case primary systems are down.
- Customers: Require transparent updates on the problem, the solution, and expected timelines. Honesty builds trust.
Prepare pre-approved message templates for common scenarios to enable fast, consistent communication under pressure. Establish redundant communication channels (e.g., social media if your website is down) and clear information flow protocols (who gathers facts, who approves messages, who sends them). Professional, timely communication shows you are in control and protects your reputation.
Exploring Modern Disaster Recovery Solutions
Disaster recovery management has been transformed by technology. Modern solutions are smarter, more flexible, and more affordable than the expensive, idle secondary data centers of the past. Technologies like cloud computing, virtualization, and automated failover systems are game-changers.
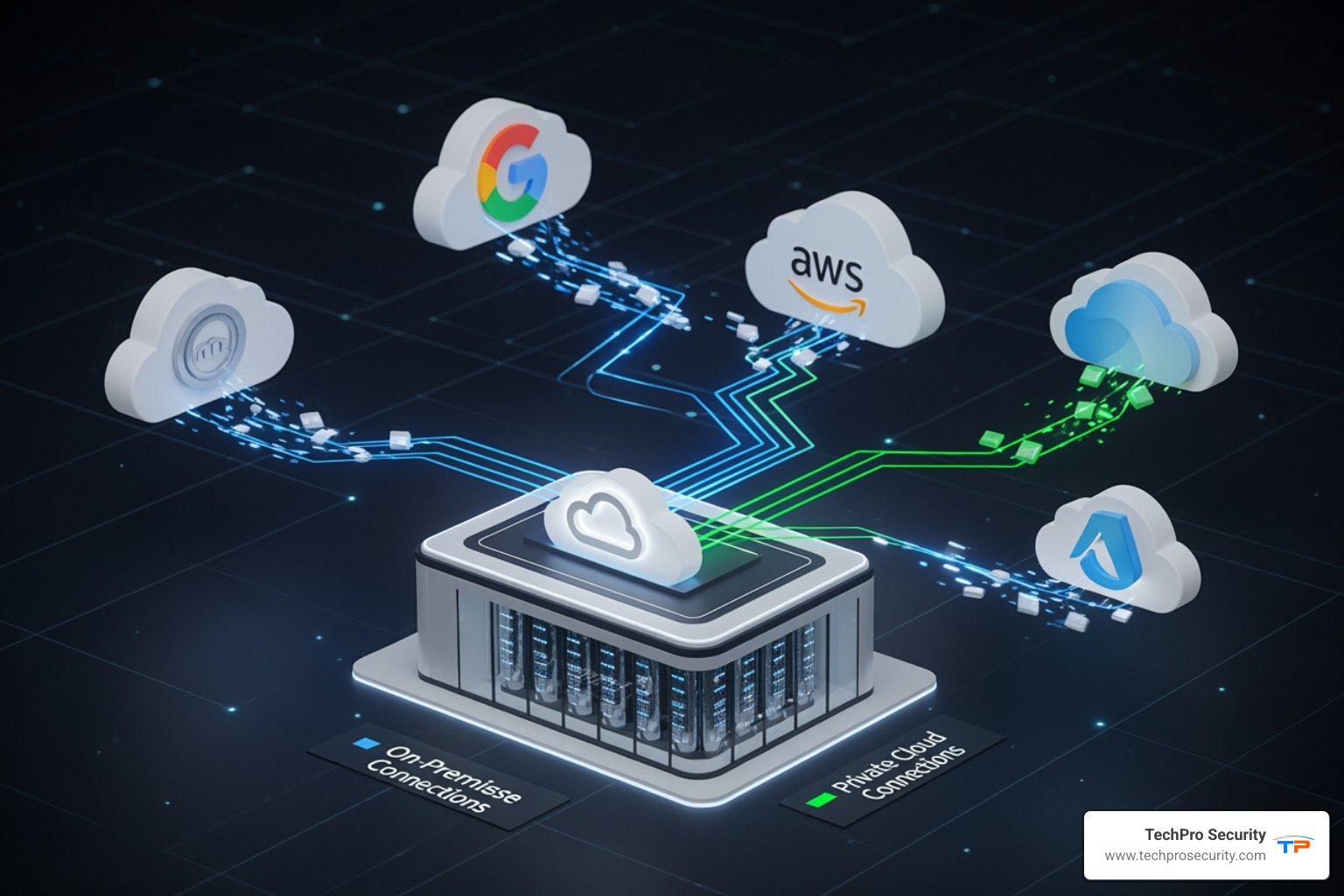

Leveraging the Cloud for Improved Recovery
Cloud computing has revolutionized disaster recovery, making enterprise-grade solutions accessible to all businesses.
- Scalability & Cost-Effectiveness: The cloud allows you to instantly scale resources up during a disaster and back down afterward, replacing massive capital expenditures with predictable operational costs.
- Geographic Redundancy: Reputable cloud providers offer data centers in different geographic regions, protecting your backups from local disasters like the hurricanes we see in South Florida.
- Reduced RTO/RPO: Cloud solutions can dramatically shorten recovery times, often to just minutes, with near-zero data loss through continuous replication.
- Automated Failover: Systems can automatically switch to a backup cloud environment without human intervention, minimizing downtime.
Our Cloud Backup Services provide this flexible, resilient approach to disaster recovery management.
Choosing the Right DR Software and Services
Selecting the right disaster recovery management solution is a strategic decision. Here’s what to consider:
- RTO and RPO Objectives: Your required recovery times and data loss tolerance will be the primary drivers of your choice. Near-instant recovery costs more but is essential for mission-critical systems.
- Replication Strategy: The best method (application, virtual machine, or storage-level) depends on your specific infrastructure and applications.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Factor in maintenance, support, training, and scaling costs over the long term.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): With a DRaaS provider, scrutinize the SLA for guaranteed RTO/RPO during an emergency and penalties if they are not met.
- Security Features: Ensure the solution includes robust encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications to protect your data during a crisis.
The complexity of these choices is why expert guidance is so valuable. Our team understands how different Disaster Recovery Planning Tools fit real-world business needs. The best solution is one that matches your specific requirements, budget, and risk tolerance.
Testing, Maintaining, and Improving Your DR Plan
A disaster recovery management plan is not a one-and-done document. It’s a living system that requires regular maintenance and testing to be effective when you need it most. As your business, technology, and threats evolve, your plan must adapt.

Best Practices for Effective Disaster Recovery Management
Effective disaster recovery management relies on proven practices to keep your plan ready for action.
- Regular Testing: Conduct tabletop exercises (walking through the plan) and full-scale simulations (actually failing over systems) to validate procedures.
- Post-Mortem Analysis: After every test, analyze what worked and what didn’t. Use these lessons to improve the plan.
- Version Control: Ensure everyone is working from the most current version of the DR plan. Outdated instructions cause chaos.
- Annual Reviews: At least once a year, review the entire plan to align it with current business priorities, technologies, and regulations.
- Focus on Consequences: Design your plan to recover from outcomes (e.g., server failure, data loss) rather than every specific cause. This creates a more flexible and useful plan.
For a comprehensive federal framework, many organizations reference the NIST Special Publication 800-34, which provides a detailed methodology for contingency planning. Our Network Management services apply this same systematic approach to your physical security infrastructure.
For more guidance, explore our Disaster Recovery Best Practices.
The Role of Training and Regular Drills
A brilliant plan is useless if your team can’t execute it. Training and drills build the competence and confidence needed in a crisis.
- Employee Readiness: All employees should know their basic role, who to contact, and where to find information during a disaster.
- Role-Specific Training: Your DR team members need hands-on practice with the systems and procedures they are responsible for.
- Simulate Real-World Scenarios: Drills uncover weaknesses that theoretical planning can miss, like a slow backup internet connection or unexpected system dependencies.
Regular training builds a “continuity culture” where preparedness is second nature. When your team has practiced their roles, confidence replaces confusion. This principle applies to physical security as well; team familiarity with access control and surveillance procedures is just as vital as the technology itself.
For structured guidance on developing training programs, refer to our NIST Guide to Test, Training, and Exercise Programs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Disaster Recovery Management
As a business owner, you likely have questions about disaster recovery management. Here are answers to some of the most common ones.
How often should a disaster recovery plan be tested?
At a minimum, you should test your plan at least once a year. However, the ideal frequency depends on your business. If downtime is extremely costly, you should test more often, perhaps quarterly.
It’s also crucial to test after any significant IT changes, such as adding new servers or major software updates. We recommend a mix of tabletop exercises for regular check-ins and full-scale simulations for annual validation.
What is the difference between disaster recovery and business continuity?
People often use these terms interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings.
- Disaster Recovery (DR) is a subset of business continuity. It is IT-focused and deals with restoring your technology infrastructure—servers, networks, data, and applications—after a disruptive event.
- Business Continuity (BC) is the broader strategy for keeping your entire business operational during a disaster. It includes DR but also covers people, processes, and facilities, such as setting up temporary workspaces or rerouting communications.
In short: DR gets your tech working again; BC keeps your business working. Learn more in our guide on Business Continuity vs. Disaster Recovery.
How do I determine the RTO and RPO for my business?
Your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) are business decisions, not just technical specs. You determine them through a Business Impact Analysis (BIA).
- To find your RTO (time): For each critical system, ask: “How long can this be down before it causes significant financial or reputational damage?” The answer is your maximum acceptable downtime.
- To find your RPO (data): Ask: “How much data can we afford to lose?” This is determined by how frequently your data changes. An e-commerce site might need an RPO of seconds, while a system with static files might tolerate an RPO of 24 hours.
The goal is to find the right balance between risk and cost. Tighter RTOs and RPOs provide more protection but require a larger investment.
Conclusion
Disasters don’t wait for a convenient time. A sudden system failure or data loss can threaten your company’s existence. This is why disaster recovery management isn’t an IT luxury—it’s a fundamental requirement for business survival.
Proactive planning transforms potential catastrophes into manageable events. By conducting a business impact analysis, setting clear recovery objectives (RTO/RPO), and building a trained response team, you create a vital safety net for your business.
Modern solutions, especially cloud-based services, have made robust disaster recovery accessible and affordable for businesses of all sizes. However, technology is only part of the solution. Regular testing and team training are what turn a plan on paper into a shield that works in a real crisis.
At TechPro Security, we understand that true resilience starts with physical security. Our expertise in cameras, access control systems, and automatic gates provides the first line of defense for your critical IT infrastructure. A perfect cloud backup is vulnerable if someone can simply walk into your server room.
With our deep experience in South Florida, we protect businesses from both digital and physical threats. The statistic is stark: more than 40% of businesses never reopen after a disaster. Don’t be one of them.
Your business deserves to be resilient. Take control of your future today. Protect your business with our expert Disaster Recovery services and build the resilience to thrive, no matter what comes your way.